Abstract
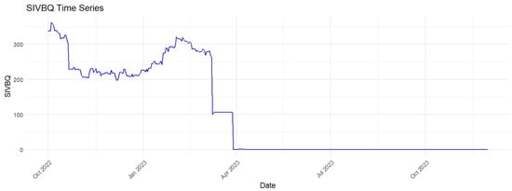
: The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) on 11 March 2023, and the subsequent depegging of the USDC stablecoin highlighted vulnerabilities in the interconnected financial ecosystem. While prior research has explored the systemic risks of stablecoins and their reliance on traditional banking, there has been limited focus on how banking sector shocks affect digital asset markets. This study addresses this gap by analyzing the impact of SVB’s collapse on the stability of major stablecoins—USDC, DAI, FRAX, and USDD—and their relationships with Bitcoin and Tether. Using daily data from October 2022 to November 2023, we found that the SVB incident triggered a series of depegging events, with varying effects across stablecoins. Our results indicate that USDC, often viewed as one of the safer stablecoins, was particularly vulnerable due to its reliance on SVB reserves. Other stablecoins experienced different impacts based on their collateral structures. These findings challenge the notion of stablecoins as inherently safe assets and underscore the need for improved risk management and regulatory oversight. Additionally, this study illustrates how machine learning models, including gradient boosting and random forests, can enhance our understanding of financial contagion and market stability.